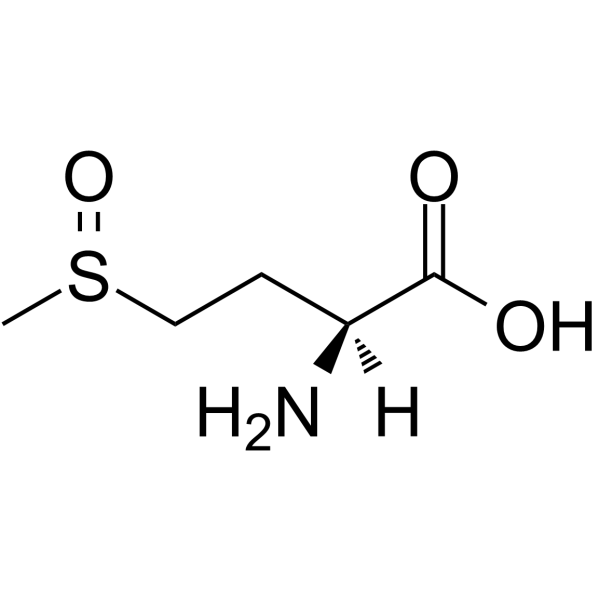
L-Methionine sulfoxide
CAS No. 3226-65-1
L-Methionine sulfoxide( H-Met(O)-OH )
Catalog No. M27086 CAS No. 3226-65-1
L-Methionine sulfoxide (H-Met(O)-OH) is a metabolite of Methionine. (H-Met(O)-OH) modulates oxidative stress and purinergic signaling parameters, and induces M1/classical macrophage polarization.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Methionine sulfoxide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-Methionine sulfoxide (H-Met(O)-OH) is a metabolite of Methionine. (H-Met(O)-OH) modulates oxidative stress and purinergic signaling parameters, and induces M1/classical macrophage polarization.
-
DescriptionL-Methionine sulfoxide (H-Met(O)-OH) is a metabolite of Methionine. (H-Met(O)-OH) modulates oxidative stress and purinergic signaling parameters, and induces M1/classical macrophage polarization.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsH-Met(O)-OH
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorERK1| ERK2| RAF
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3226-65-1
-
Formula Weight165.21
-
Molecular FormulaC5H11NO3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 100 mg/mL (605.29 mM)
-
SMILESCS(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.CAPONIGRO, et al. THERAPEUTIC COMBINATIONS COMPRISING A RAF INHIBITOR AND A ERK INHIBITOR. WO2018051306A1.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nα-Acetyl-L-lysine
N-Alpha-acetyllysine is a N-acetylated amino acid. It is a normal constituent of human urine with concentrations in normal samples too small to allow its routine detection; however it has been found at increased levels in the urine of a patient with aminoacylase I deficiency.
-
Adenosine triphospha...
Adenosine triphosphate is an adenine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety.
-
5-Methyltetrahydrofo...
5-Methyltetrahydrofolic acid is a biologically active form of folic acid and a methylated derivate of tetrahydrofolate.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


